編寫“Hello World”程序
下方將展示如何在單板上運行第一個應用程序,其中包括新建應用程序、編譯、燒寫、運行等步驟,最終輸出“Hello World!”。
前提條件
已參考[創建工程并獲取源碼],創建RK3568開發板的源碼工程。
示例目錄
拉取openharmony項目代碼,在代碼根目錄創建sample子系統文件夾,在子系統目錄下創建hello部件文件夾,hello文件夾中創建hello源碼目錄,構建文件BUILD.gn及部件配置文件bundle.json。 示例完整目錄如下。
HarmonyOS與OpenHarmony鴻蒙文檔籽料:mau123789是v直接拿
sample/hello
│── BUILD.gn
│── include
│ └── helloworld.h
│── src
│ └── helloworld.c
├── bundle.json
build
└── subsystem_config.json
vendor/hihope
└── rk3568
└── config.json
開發步驟
鴻蒙開發指導文檔:[gitee.com/li-shizhen-skin/harmony-os/blob/master/README.md]
請在源碼目錄中通過以下步驟創建“Hello World”應用程序。
創建目錄,編寫業務代碼。
新建sample/hello/src/helloworld.c目錄及文件,代碼如下所示,用戶可以自定義修改打印內容(例如:修改World為OHOS)。其中helloworld.h包含字符串打印函數HelloPrint的聲明。當前應用程序可支持標準C及C++的代碼開發。#include < stdio.h > #include "helloworld.h" int main(int argc, char **argv) { HelloPrint(); return 0; } void HelloPrint() { printf("nn"); printf("nttHello World!n"); printf("nn"); }再添加頭文件sample/hello/include/helloworld.h,代碼如下所示。
#ifndef HELLOWORLD_H #define HELLOWORLD_H #ifdef __cplusplus #if __cplusplus extern "C" { #endif #endif void HelloPrint(); #ifdef __cplusplus #if __cplusplus } #endif #endif #endif // HELLOWORLD_H新建編譯組織文件。
新建sample/hello/BUILD.gn,創建方法可參考:[模塊配置規則]。
模塊
模塊配置規則
編譯子系統通過模塊、部件和產品三層配置來實現編譯和打包。模塊就是編譯子系統的一個目標,包括(動態庫、靜態庫、配置文件、預編譯模塊等)。模塊要定義屬于哪個部件,一個模塊只能歸屬于一個部件。OpenHarmony使用定制化的Gn模板來配置模塊規則,Gn語法相關的基礎知識請參考[官網手冊]
以下是常用的模塊配置規則:
# C/C++模板
ohos_shared_library
ohos_static_library
ohos_executable
ohos_source_set
# 預編譯模板:
ohos_prebuilt_executable
ohos_prebuilt_shared_library
ohos_prebuilt_static_library
#hap模板
ohos_hap
ohos_app_scope
ohos_js_assets
ohos_resources
#rust模板
ohos_rust_executable
ohos_rust_shared_library
ohos_rust_static_library
ohos_rust_proc_macro
ohos_rust_shared_ffi
ohos_rust_static_ffi
ohos_rust_cargo_crate
ohos_rust_systemtest
ohos_rust_unittest
ohos_rust_fuzztest
#其他常用模板
#配置文件
ohos_prebuilt_etc
#sa配置
ohos_sa_profile
ohos開頭的模板與內建模板的差異主要在于:推薦使用ohos定制模板。
C/C++模板示例
ohos開頭的模板對應的.gni文件路徑在:openharmony/build/templates/cxx/cxx.gni。
ohos_shared_library示例
import("http://build/ohos.gni")
ohos_shared_library("helloworld") {
sources = ["file"]
include_dirs = [] # 如有重復頭文件定義,優先使用前面路徑頭文件。
cflags = [] # 如重復沖突定義,后面的參數優先生效,也就是該配置項中優先生效。
cflags_c = []
cflags_cc = []
ldflags = [] # 如重復沖突定義,前面參數優先生效,也就是ohos_template中預制參數優先生效。
configs = []
deps = [] # 部件內模塊依賴
external_deps = [ # 跨部件模塊依賴定義
"part_name:module_name", # 定義格式為 "部件名:模塊名稱"。
] # 這里依賴的模塊必須是依賴的部件聲明在inner_kits中的模塊。
output_name = [string] # 模塊輸出名
output_extension = [] # 模塊名后綴
module_install_dir = "" # 模塊安裝路徑,缺省在/system/lib64或/system/lib下; 模塊安裝路徑從system/,vendor/后開始指定。
relative_install_dir = "" # 模塊安裝相對路徑,相對于/system/lib64或/system/lib;如果有module_install_dir配置時,該配置不生效。
part_name = "" # 必選,所屬部件名稱
output_dir
# Sanitizer配置,每項都是可選的,默認為false/空。
sanitize = {
# 各個Sanitizer開關
cfi = [boolean] # 控制流完整性檢測
cfi_cross_dso = [boolean] # 開啟跨so調用的控制流完整性檢測
integer_overflow = [boolean] # 整數溢出檢測
boundary_sanitize = [boolean] # 邊界檢測
ubsan = [boolean] # 部分ubsan選項
all_ubsan = [boolean] # 全量ubsan選項
...
debug = [boolean] # 調測模式
blocklist = [string] # 屏蔽名單路徑
}
testonly = [boolean]
license_as_sources = []
license_file = [] # 后綴名是.txt的文件
remove_configs = []
no_default_deps = []
install_images = []
install_enable = [boolean]
symlink_target_name = []
version_script = []
use_exceptions = []
}
ohos_static_library示例
import("http://build/ohos.gni")
ohos_static_library("helloworld") {
sources = ["file"] # 后綴名是.c的相關文件
include_dirs = ["dir"] # 包含目錄
configs = [] # 配置
deps = [] # 部件內模塊依賴
part_name = "" # 部件名稱
subsystem_name = "" # 子系統名稱
cflags = []
external_deps = [ # 跨部件模塊依賴定義,
"part_name:module_name", # 定義格式為 "部件名:模塊名稱"
] # 這里依賴的模塊必須是依賴的部件聲明在inner_kits中的模塊。
lib_dirs = []
public_configs = []
# Sanitizer配置,每項都是可選的,默認為false/空
sanitize = {
# 各個Sanitizer開關
cfi = [boolean] # 控制流完整性檢測
cfi_cross_dso = [boolean] # 開啟跨so調用的控制流完整性檢測
integer_overflow = [boolean] # 整數溢出檢測
boundary_sanitize = [boolean] # 邊界檢測
ubsan = [boolean] # 部分ubsan選項
all_ubsan = [boolean] # 全量ubsan選項
...
debug = [boolean] # 調測模式
blocklist = [string] # 屏蔽名單路徑
}
remove_configs = []
no_default_deps = []
license_file = [] # 后綴名是.txt的文件
license_as_sources = []
use_exceptions = []
}
ohos_executable示例
import("http://build/ohos.gni")
ohos_executable("helloworld") {
configs = [] # 配置
part_name = "" # 部件名稱
subsystem_name = "" # 子系統名稱
deps = [] # 部件內模塊依賴
external_deps = [ # 跨部件模塊依賴定義,
"part_name:module_name", # 定義格式為 "部件名:模塊名稱"
] # 這里依賴的模塊必須是依賴的部件聲明在inner_kits中的模塊。
ohos_test = []
test_output_dir = []
# Sanitizer配置,每項都是可選的,默認為false/空
sanitize = {
# 各個Sanitizer開關
cfi = [boolean] # 控制流完整性檢測
cfi_cross_dso = [boolean] # 開啟跨so調用的控制流完整性檢測
integer_overflow = [boolean] # 整數溢出檢測
boundary_sanitize = [boolean] # 邊界檢測
ubsan = [boolean] # 部分ubsan選項
all_ubsan = [boolean] # 全量ubsan選項
...
debug = [boolean] # 調測模式
blocklist = [string] # 屏蔽名單路徑
}
testonly = [boolean]
license_as_sources = []
license_file = [] # 后綴名是.txt的文件
remove_configs = []
static_link = []
install_images = []
module_install_dir = "" # 模塊安裝路徑,從system/,vendor/后開始指定
relative_install_dir = ""
symlink_target_name = []
output_dir = [directory] # 存放輸出文件的目錄
install_enable = [boolean]
version_script = []
use_exceptions = []
}
ohos_source_set示例
import("http://build/ohos.gni")
ohos_source_set("helloworld") {
sources = ["file"] # 后綴名是.c的相關文件
include_dirs = [] # 包含目錄
configs = [] # 配置
public = [] # .h類型頭文件
defines = []
public_configs = []
part_name = "" # 部件名稱
subsystem_name = "" # 子系統名稱
deps = [] # 部件內模塊依賴
external_deps = [ # 跨部件模塊依賴定義,
"part_name:module_name", # 定義格式為 "部件名:模塊名稱"
] # 這里依賴的模塊必須是依賴的部件聲明在inner_kits中的模塊
# Sanitizer配置,每項都是可選的,默認為false/空
sanitize = {
# 各個Sanitizer開關
cfi = [boolean] # 控制流完整性檢測
cfi_cross_dso = [boolean] # 開啟跨so調用的控制流完整性檢測
integer_overflow = [boolean] # 整數溢出檢測
boundary_sanitize = [boolean] # 邊界檢測
ubsan = [boolean] # 部分ubsan選項
all_ubsan = [boolean] # 全量ubsan選項
...
debug = [boolean] # 調測模式
blocklist = [string] # 屏蔽名單路徑
}
testonly = [boolean]
license_as_sources = []
license_file = []
remove_configs = []
no_default_deps = []
license_file = [] # 后綴名是.txt的文件
license_as_sources = []
use_exceptions = []
}
注意 :
- 只有sources和part_name是必選,其他都是可選的;
- Sanitizer配置詳見:[Sanitizer使用說明]
預編譯模板示例
預編譯模板的.gni相關文件路徑在:openharmony/build/templates/cxx/prebuilt.gni。
ohos_prebuilt_executable示例
import("http://build/ohos.gni")
ohos_prebuilt_executable("helloworld") {
source = "file" # 源
output = []
install_enable = [boolean]
deps = [] # 部件內模塊依賴
public_configs = []
subsystem_name = "" # 子系統名
part_name = "" # 部件名
testonly = [boolean]
visibility = []
install_images = []
module_install_dir = "" # 模塊安裝路徑,從system/,vendor/后開始指定
relative_install_dir = "" # 模塊安裝相對路徑,相對于system/etc;如果有module_install_dir配置時,該配置不生效。
symlink_target_name = []
license_file = [] # 后綴名是.txt的文件
license_as_sources = []
}
ohos_prebuilt_shared_library示例
import("http://build/ohos.gni")
ohos_prebuilt_shared_library("helloworld") {
source = "file" # 一般是后綴為.so的文件
output = []
install_enable = [boolean]
deps = [] # 部件內模塊依賴
public_configs = []
subsystem_name = "" # 子系統名
part_name = "" # 部件名
testonly = [boolean]
visibility = []
install_images = []
module_install_dir = "" # 模塊安裝路徑,從system/,vendor/后開始指定
relative_install_dir = "" # 模塊安裝相對路徑,相對于system/etc;如果有module_install_dir配置時,該配置不生效。
symlink_target_name = [string]
license_file = [string] # 后綴名是.txt的文件
license_as_sources = []
}
ohos_prebuilt_static_library示例
import("http://build/ohos.gni")
ohos_prebuilt_static_library("helloworld") {
source = "file" # 一般是后綴為.so的文件
output = []
deps = [] # 部件內模塊依賴
public_configs = []
subsystem_name = "" # 子系統名
part_name = "" # 部件名
testonly = [boolean]
visibility = []
license_file = [string] # 后綴名是.txt的文件
license_as_sources = []
}
注意 :只有sources和part_name是必選,其他都是可選的。
Hap模板
hap模板詳見:[ HAP編譯構建指導]
Rust模板
rust模板詳見:[ Rust模塊配置規則和指導]
其他常用模板
ohos_prebuilt_etc示例:
import("http://build/ohos.gni")
ohos_prebuilt_etc("helloworld") {
# ohos_prebuilt_etc模板最常用屬性:
source = "file" # 指定單個原文件
module_install_dir = "" # 模塊安裝路徑,從system/,vendor/后開始指定
subsystem_name = "" # 子系統名
part_name = "" # 必選,所屬部件名稱
install_images = []
relative_install_dir = "" # 模塊安裝相對路徑,相對于system/etc;如果有module_install_dir配置時,該配置不生效。
# ohos_prebuilt_etc模板不常用屬性:
deps = [] # 部件內模塊依賴
testonly = [boolean]
visibility = []
public_configs = []
symlink_target_name = [string]
license_file = [string]
license_as_sources = []
}
ohos_sa_profile示例:
import("http://build/ohos.gni")
ohos_sa_profile("helloworld") {
sources = [".xml"] # xml文件
part_name = "" # 部件名
subsystem_name = "" # 子系統名
}
注意 :只有sources和part_name是必選,其他都是可選的。
新增并編譯模塊
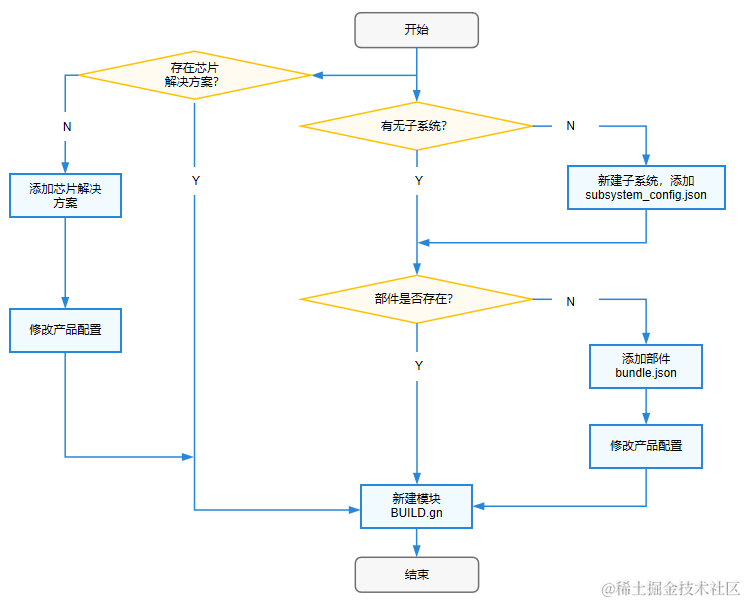
新建模塊可以分為以下三種情況。主要的添加邏輯如下面的流程圖所示,若沒有子系統則需新建子系統并在該子系統的部件下添加模塊,若沒有部件則需新建部件并在其中添加模塊,否則直接在原有部件中添加模塊即可,需要注意的是芯片解決方案作為特殊部件是沒有對應子系統的。
- 在原有部件中添加一個模塊
- 新建部件并在其中添加模塊
- 新建子系統并在該子系統的部件下添加模塊
在原有部件中添加一個模塊
- 在模塊目錄下配置BUILD.gn,根據模板類型選擇對應的gn模板。
- 修改bundle.json配置文件。
{ "name": "@ohos/< component_name >", # HPM部件英文名稱,格式"@組織/部件名稱" "description": "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx", # 部件功能一句話描述 "version": "3.1", # 版本號,版本號與OpenHarmony版本號一致 "license": "MIT", # 部件License "publishAs": "code-segment", # HPM包的發布方式,當前默認都為code-segment "segment": { "destPath": "third_party/nghttp2" }, # 發布類型為code-segment時為必填項,定義發布類型code-segment的代碼還原路徑(源碼路徑)。 "dirs": {}, # HPM包的目錄結構,字段必填內容可以留空 "scripts": {}, # HPM包定義需要執行的腳本,字段必填,值非必填 "licensePath": "COPYING", "readmePath": { "en": "README.rst" }, "component": { # 部件屬性 "name": "< component_name >", # 部件名稱 "subsystem": , # 部件所屬子系統 "syscap": [], # 部件為應用提供的系統能力 "features": [], # 部件對外的可配置特性列表,一般與build中的sub_component對應,可供產品配置。 "adapted_system_type": [], # 輕量(mini)小型(small)和標準(standard),可以是多個 "rom": "xxxKB" # ROM基線,沒有基線寫當前值 "ram": "xxxKB", # RAM基線,沒有基線寫當前值 "deps": { "components": [], # 部件依賴的其他部件 "third_party": [] # 部件依賴的三方開源軟件 }, "build": { # 編譯相關配置 "sub_component": [ "http://foundation/arkui/napi:napi_packages", # 原有模塊1 "http://foundation/arkui/napi:napi_packages_ndk" # 原有模塊2 "http://foundation/arkui/napi:new" # 新增模塊new ], # 部件編譯入口,模塊在此處配置 "inner_kits": [], # 部件間接口 "test": [] # 部件測試用例編譯入口 } } }
注意 :無論哪種方式該bundle.json文件均在對應子系統所在文件夾下。
- 成功添加驗證:編譯完成后打包到image中去,生成對應的so文件或者二進制文件。
新建部件并在其中添加一個模塊
- 在模塊目錄下配置BUILD.gn,根據模板類型選擇對應的gn模板。這一步與在原有部件中添加一個模塊的方法基本一致,只需注意該模塊對應BUILD.gn文件中的part_name為新建部件的名稱即可。
- 新建一個bundle.json文件,bundle.json文件均在對應子系統所在文件夾下。
- 在vendor/{product_company}/{product-name}/config.json中添加對應的部件,直接添加到原有部件后即可。
"subsystems": [ { "subsystem": "部件所屬子系統名", "components": [ { "component": "部件名1", "features":[] }, # 子系統下的原有部件1 { "component": "部件名2", "features":[] }, # 子系統下的原有部件2 { "component": "部件名new", "features":[] } # 子系統下的新增部件new ] }, . ] - 成功添加驗證:編譯完成后打包到image中去,生成對應的so文件或者二進制文件。
新建子系統并在該子系統的部件下添加模塊
在模塊目錄下配置BUILD.gn,根據模板類型選擇對應的gn模板。這一步與新建部件并在其中添加模塊中對應的步驟并無區別。
在新建的子系統目錄下每個部件對應的文件夾下創建bundle.json文件,定義部件信息。這一步與新建部件并在其中添加模塊中對應的步驟并無區別。
修改build目錄下的subsystem_config.json文件。
{ "子系統名1": { # 原有子系統1 "path": "子系統目錄1", "name": "子系統名1" }, "子系統名2": { # 原有子系統2 "path": "子系統目錄2", "name": "子系統名2" }, "子系統名new": { # 新增子系統new "path": "子系統目錄new", "name": "子系統名new" }, }該文件定義了有哪些子系統以及這些子系統所在文件夾路徑,添加子系統時需要說明子系統path與name,分別表示子系統路徑和子系統名。
在vendor/{product_company}/{product-name}目錄下的產品配置如product-name是hispark_taurus_standard時,在config.json中添加對應的部件,直接添加到原有部件后即可。
"subsystems": [ { "subsystem": "arkui", # 原有的子系統名 "components": [ # 單個子系統下的所有部件集合 { "component": "ace_engine_standard", # 原有的部件名 "features": [] }, { "component": "napi", # 原有的部件名 "features": [] } { "component": "component_new1", # 原有子系統新增的的部件名component_new1 "features": [] } ] }, { "subsystem": "subsystem_new", # 新增的子系統名 "components": [ { "component": "component_new2", # 新增子系統新增的的部件名component_new2 "features": [] } ] }, ]成功添加驗證:編譯完成后打包到image中去,生成對應的so文件或者二進制文件。
編譯模塊
主要有兩種編譯方式,[命令行方式和hb方式],這里以命令行方式為例。
模塊可以使用“--build-target 模塊名"單獨編譯,編譯命令如下:
./build.sh --build-target 模塊名
也可以編譯相應產品,以編譯hispark_taurus_standard為例,編譯命令如下:
./build.sh --product-name hispark_taurus_standard --build-target 模塊名 --ccache
還可以編譯模塊所在的部件:
./build.sh --product-name hispark_taurus_standard --build-target musl --build-target 模塊名 --ccache
創建 BUILD.gn內容如下所示:
import("http://build/ohos.gni") # 導入編譯模板
ohos_executable("helloworld") { # 可執行模塊
sources = [ # 模塊源碼
"src/helloworld.c"
]
include_dirs = [ # 模塊依賴頭文件目錄
"include"
]
cflags = []
cflags_c = []
cflags_cc = []
ldflags = []
configs = []
deps =[] # 部件內部依賴
part_name = "hello" # 所屬部件名稱,必選
install_enable = true # 是否默認安裝(缺省默認不安裝),可選
}
- 新建部件配置規則文件
新建sample/hello/bundle.json文件,添加sample部件描述,創建方法可參考:[部件配置規則]
部件配置規則
部件的bundle.json放在部件源碼的根目錄下。以泛sensor子系統的sensor服務部件為例,部件屬性定義描述文件字段說明如下:
{
"name": "@ohos/sensor_lite", # HPM部件英文名稱,格式"@組織/部件名稱"
"description": "Sensor services", # 部件功能一句話描述
"version": "3.1", # 版本號,版本號與OpenHarmony版本號一致
"license": "MIT", # 部件License
"publishAs": "code-segment", # HPM包的發布方式,當前默認都為code-segment
"segment": {
"destPath": ""
}, # 發布類型為code-segment時為必填項,定義發布類型code-segment的代碼還原路徑(源碼路徑)
"dirs": {"base/sensors/sensor_lite"}, # HPM包的目錄結構,字段必填內容可以留空
"scripts": {}, # HPM包定義需要執行的腳本,字段必填,值非必填
"licensePath": "COPYING",
"readmePath": {
"en": "README.rst"
},
"component": { # 部件屬性
"name": "sensor_lite", # 部件名稱
"subsystem": "", # 部件所屬子系統
"syscap": [], # 部件為應用提供的系統能力
"features": [], # 部件對外的可配置特性列表,一般與build中的sub_component對應,可供產品配置
"adapted_system_type": [], # 輕量(mini)小型(small)和標準(standard),可以是多個
"rom": "92KB", # 部件ROM值
"ram": "~200KB", # 部件RAM估值
"deps": {
"components": [ # 部件依賴的其他部件
"samgr_lite",
"ipc_lite"
],
"third_party": [ # 部件依賴的三方開源軟件
"bounds_checking_function"
],
"hisysevent_config": [] # 部件HiSysEvent打點配置文件編譯入口
}
"build": { # 編譯相關配置
"sub_component": [
""//base/sensors/sensor_lite/services:sensor_service"", # 部件編譯入口
], # 部件編譯入口,模塊在此處配置
"inner_kits": [], # 部件間接口
"test": [] # 部件測試用例編譯入口
}
}
}
注意 :lite上舊的部件在build/lite/components目錄下對應子系統的json文件中,路徑規則為: {領域}/{子系統}/{部件} ,部件目錄樹規則如下:
component
├── interfaces
│ ├── innerkits # 系統內接口,部件間使用
│ └── kits # 應用接口,應用開發者使用
├── frameworks # framework實現
├── services # service實現
└── BUILD.gn # 部件編譯腳本
部件配置中需要配置部件的名稱、源碼路徑、功能簡介、是否必選、編譯目標、RAM、ROM、編譯輸出、已適配的內核、可配置的特性和依賴等屬性定義。
注意 :部件配置中HiSysEvent打點配置文件使用說明,請參考文檔[HiSysEvent打點配置]。
新增部件時需要在對應子系統json文件中添加相應的部件定義。產品所配置的部件必須在某個子系統中被定義過,否則會校驗失敗。
新增并編譯部件
添加部件。 本節以添加一個自定義的部件為例,描述如何編譯部件,編譯庫、編譯可執行文件等。
示例部件partA由feature1、feature2和feature3組成,feature1的編譯目標為一個動態庫,feature2的目標為一個可執行程序,feature3的目標為一個etc配置文件。
示例部件partA的配置需要添加到一個子系統中,本次示例將添加到subsystem_examples子系統中(subsystem_examples子系統定義在test/examples/目錄)。
示例部件partA的完整目錄結構如下:test/examples/partA ├── feature1 │ ├── BUILD.gn │ ├── include │ │ └── helloworld1.h │ └── src │ └── helloworld1.cpp ├── feature2 │ ├── BUILD.gn │ ├── include │ │ └── helloworld2.h │ └── src │ └── helloworld2.cpp └── feature3 ├── BUILD.gn └── src └── config.conf示例1:編寫動態庫gn腳本test/examples/partA/feature1/BUILD.gn,示例如下:
config("helloworld_lib_config") { include_dirs = [ "include" ] } ohos_shared_library("helloworld_lib") { sources = [ "include/helloworld1.h", "src/helloworld1.cpp", ] public_configs = [ ":helloworld_lib_config" ] part_name = "partA" }示例2:編寫可執行文件gn腳本test/examples/partA/feature2/BUILD.gn,示例如下:
ohos_executable("helloworld_bin") { sources = [ "src/helloworld2.cpp" ] include_dirs = [ "include" ] deps = [ # 依賴部件內模塊 "../feature1:helloworld_lib" ] external_deps = [ "partB:module1" ] # (可選)如果有跨部件的依賴,格式為“部件名:模塊名” install_enable = true # 可執行程序缺省不安裝,需要安裝時需要指定 part_name = "partA" }示例3:編寫etc模塊gn腳本test/examples/partA/feature3/BUILD.gn,示例如下:
ohos_prebuilt_etc("feature3_etc") { source = "src/config.conf" relative_install_dir = "init" #可選,模塊安裝相對路徑,相對于默認安裝路徑;默認在/system/etc目錄 part_name = "partA" }示例4:在部件的bundle.json中添加模塊配置:test/examples/bundle.json。每個部件都有一個bundle.json配置文件,在部件的根目錄下。示例見:[部件的bundle.json]
將部件添加到產品配置中。 在產品的配置中添加部件,產品對應的配置文件://vendor/{product_company}/{product-name}/config.json。下面以vendor/hisilicon/hispark_taurus_standard/config.json為例:
{ "product_name": "hispark_taurus_standard", "device_company": "hisilicon", "device_build_path": "device/board/hisilicon/hispark_taurus/linux", "target_cpu": "arm", "type": "standard", "version": "3.0", "board": "hispark_taurus", "inherit": [ "productdefine/common/base/standard_system.json", "productdefine/common/inherit/ipcamera.json" ], "enable_ramdisk": true, "subsystems": [ { "subsystem": "subsystem_examples", # 部件所屬子系統 "components": [ { "component": "partA", # 部件名稱 "features": [] # 部件對外的可配置特性列表 } ] }, ······ }從中可以看出產品名稱、芯片廠家等;inherit指出依賴的通用組件;subsystems指出通用組件以外的部件。
在產品配置文件中添加 "subsystem_examples:partA",表示該產品中會編譯并打包partA到版本中。
編譯。 主要有兩種編譯方式,[命令行方式和hb方式],下面以命令行方式為例:
部件可以使用"--build-target 部件名"進行單獨編譯,以編譯產品hispark_taurus_standard的musl部件為例,編譯命令如下:./build.sh --product-name hispark_taurus_standard --build-target musl --ccache也可以編譯相應產品,以編譯hispark_taurus_standard為例,編譯命令如下:
./build.sh --product-name hispark_taurus_standard --ccache編譯輸出。 編譯所生成的文件都歸檔在out/hispark_taurus/目錄下,結果鏡像輸出在 out/hispark_taurus/packages/phone/images/ 目錄下。
bundle.json內容如下所示。{ "name": "@ohos/hello", "description": "Hello world example.", "version": "3.1", "license": "Apache License 2.0", "publishAs": "code-segment", "segment": { "destPath": "sample/hello" }, "dirs": {}, "scripts": {}, "component": { "name": "hello", "subsystem": "sample", "syscap": [], "features": [], "adapted_system_type": [ "mini", "small", "standard" ], "rom": "10KB", "ram": "10KB", "deps": { "components": [], "third_party": [] }, "build": { "sub_component": [ "http://sample/hello:helloworld" ], "inner_kits": [], "test": [] } } }bundle.json文件包含兩個部分,第一部分描述該部件所屬子系統的信息,第二部分component則定義該部件構建相關配置。添加的時候需要指明該部件包含的模塊sub_component,假如有提供給其它部件的接口,需要在inner_kits中說明,假如有測試用例,需要在test中說明,inner_kits與test沒有也可以不添加。
修改子系統配置文件。
在build/subsystem_config.json中添加新建的子系統的配置。修改方法可參考:[子系統配置規則]
子系統配置規則
通過build倉下的subsystem_config.json可以查看所有子系統的配置規則。
{
"arkui": {
"path": "foundation/arkui", # 路徑
"name": "arkui" # 子系統名
},
"ai": {
"path": "foundation/ai",
"name": "ai"
},
"account": {
"path": "base/account",
"name": "account"
},
"distributeddatamgr": {
"path": "foundation/distributeddatamgr",
"name": "distributeddatamgr"
},
"security": {
"path": "base/security",
"name": "security"
},
...
}
子系統的配置規則主要是在build/subsystem_config.json中指定子系統的路徑和子系統名稱。
新增子系統的配置如下所示。
"sample": {
"path": "sample",
"name": "sample"
},
修改產品配置文件。
說明: OpenHarmony-v3.2-Beta2之前版本,RK3568的產品配置文件為productdefine/common/products/rk3568.json;從OpenHarmony-v3.2-Beta2版本開始,RK3568的產品配置文件為vendor/hihope/rk3568/config.json。
- 3.2-Beta2之前版本
在productdefine/common/products/rk3568.json中添加對應的hello部件,直接添加到原有部件后即可。"usb:usb_manager_native":{}, "applications:prebuilt_hap":{}, "sample:hello":{}, "wpa_supplicant-2.9:wpa_supplicant-2.9":{}, - 3.2-Beta2及之后版本
在vendor/hihope/rk3568/config.json中添加對應的hello部件,直接添加到原有部件后即可。{ "subsystem": "sample", "components": [ { "component": "hello", "features": [] } ] },
- 3.2-Beta2之前版本
審核編輯 黃宇
-
開發板
+關注
關注
25文章
5613瀏覽量
103434 -
鴻蒙
+關注
關注
59文章
2569瀏覽量
43880 -
HarmonyOS
+關注
關注
80文章
2134瀏覽量
32473 -
OpenHarmony
+關注
關注
29文章
3846瀏覽量
18323
發布評論請先 登錄
鴻蒙OpenHarmony【標準系統編譯】 (基于RK3568開發板)
鴻蒙OpenHarmony【標準系統 編寫“Hello World”程序】(基于RK3568開發板)

鴻蒙OpenHarmony南向/北向快速開發教程-迅為RK3568開發板
迅為RK3568開發板鴻蒙OpenHarmony系統固件燒寫步驟
如何在RK3568開發板上面運行OpenHarmony標準系統
標準系統:KHDVK-3568A智慧屏開發套件(RK3568)
RK3568開發板上絲滑體驗OpenHarmony標準系統

OpenHarmony:全流程講解如何編寫ADC平臺驅動以及應用程序

基于ArkTS語言的OpenHarmony APP應用開發:HelloOpenharmony

【北京迅為】iTOP-RK3568開發板鴻蒙OpenHarmony系統南向驅動開發實操-HDF驅動配置UART






 鴻蒙OpenHarmony【標準系統編寫“Hello World”程序】 (基于RK3568開發板)
鴻蒙OpenHarmony【標準系統編寫“Hello World”程序】 (基于RK3568開發板)














評論