金屬探測器,Metal detectors
關(guān)鍵字:金屬探測器,探測器電路,金屬探測器電路

The circuit described here is that of a metal detector. The opera- tion of the circuit is based on superheterodyning principle which is commonly used in superhet receivers. The circuit utilises two RF oscillators. The frequencies of both oscillators are fixed at 5.5 MHz. The first RF oscillator comprises transistor T1 (BF 494) and a 5.5MHz ceramic filter commonly used in TV sound-IF section. The second oscillator is a Colpitt’s oscillator realised with the help of transistor T3 (BF494) and inductor L1 (whose construction details follow) shunted by trimmer capacitor VC1. These two oscillators’ frequencies (say Fx and Fy) are mixed in the mixer transistor T2 (another BF 494) and the difference or the beat frequency (Fx-Fy) output from collector of transistor T2 is connected to detector stage comprising diodes D1 and D2 (both OA 79). The output is a pulsating DC which is passed through a low-pass filter realised with the help of a 10k resistor R12 and two 15nF capacitors C6 and C10. It is then passed to AF amplifier IC1 (2822M) via volume
control VR1 and the output is fed to an 8-ohm/1W speaker. The inductor L1 can be constructed using 15 turns of 25SWG wire on a 10cm (4-inch) diameter air-core former and then cementing it with insulating varnish. For proper operation of the circuit it is critical that frequencies of both the oscillators are the same so as to obtain zero beat in the absence of any metal in the near vicinity of the circuit. The alignment of oscillator 2 (to match oscillator 1 frequency) can be done with the help of trimmer capacitor VC1. When the two frequencies are equal, the beat frequency is zero, i.e. beat frquency=Fx-Fy=0, and thus there is no sound from the loudspeaker. When search coil L1 passes over metal, the metal changes its inductance, thereby changing the second oscillator’s frequency. So now Fx-Fy is not zero and the loudspeaker sounds. Thus one is able to detect presence of metal
control VR1 and the output is fed to an 8-ohm/1W speaker. The inductor L1 can be constructed using 15 turns of 25SWG wire on a 10cm (4-inch) diameter air-core former and then cementing it with insulating varnish. For proper operation of the circuit it is critical that frequencies of both the oscillators are the same so as to obtain zero beat in the absence of any metal in the near vicinity of the circuit. The alignment of oscillator 2 (to match oscillator 1 frequency) can be done with the help of trimmer capacitor VC1. When the two frequencies are equal, the beat frequency is zero, i.e. beat frquency=Fx-Fy=0, and thus there is no sound from the loudspeaker. When search coil L1 passes over metal, the metal changes its inductance, thereby changing the second oscillator’s frequency. So now Fx-Fy is not zero and the loudspeaker sounds. Thus one is able to detect presence of metal
聲明:本文內(nèi)容及配圖由入駐作者撰寫或者入駐合作網(wǎng)站授權(quán)轉(zhuǎn)載。文章觀點僅代表作者本人,不代表電子發(fā)燒友網(wǎng)立場。文章及其配圖僅供工程師學習之用,如有內(nèi)容侵權(quán)或者其他違規(guī)問題,請聯(lián)系本站處理。
舉報投訴
發(fā)布評論請先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
熱點推薦
VirtualLab:通用探測器
摘要
通用探測器是VirtualLab Fusion中來評估和輸出電磁場任何信息的最通用工具。它能夠提供不同域(空間域和空間頻域)和坐標系(場與探測器位置坐標系)的信息。此外,通過使用非常靈活的內(nèi)置
發(fā)表于 06-12 08:59
VirtualLab Fusion應(yīng)用:用于光波導系統(tǒng)的均勻性探測器
性探測器,可以進行所需的研究。在本文件中,我們將演示可用的選項以及如何操作均勻性探測器。
案例演示
均勻性探測器
探測器功能:相干參數(shù)
?如果存在多個相干模式,則重疊的模可以相干
發(fā)表于 02-08 08:57
用于光波導系統(tǒng)的均勻性探測器
提供了均勻性探測器,可以進行所需的研究。在本文件中,我們將演示可用的選項以及如何操作均勻性探測器。
**案例演示 **
**均勻性探測器
**
**探測器功能:相干參數(shù) **
?如
發(fā)表于 12-20 10:30
不同類型金屬探測器比較
金屬探測器技術(shù)的發(fā)展為人類提供了一種有效的工具,用于探測地下或隱藏的金屬物體。隨著技術(shù)的進步,市場上出現(xiàn)了多種類型的金屬
如何提高金屬探測器探測率
要提高金屬探測器的探測率,可以從以下幾個方面入手: 一、選擇合適的金屬探測器 技術(shù)性能 :選擇技術(shù)性能先進的
金屬探測器的常見故障及解決方法
金屬探測器在長期使用過程中,可能會遇到各種故障。以下是一些常見的故障及其解決方法: 一、開機報警或震動不停 現(xiàn)象 :開機1~2秒后報警或震動不停。 原因 :一般因靈敏度過高和電力不足會出現(xiàn)這種現(xiàn)象
金屬探測器使用技巧 水下金屬探測器使用方法
金屬探測器的使用技巧和水下金屬探測器的使用方法分別如下: 金屬探測器的使用技巧 預熱 :大多數(shù)儀
雷達探測器的工作原理 雷達探測器與激光探測器區(qū)別
雷達探測器是一種利用雷達技術(shù)來檢測和跟蹤目標的設(shè)備。它的工作原理基于電磁波的發(fā)射和接收。以下是雷達探測器的基本工作原理: 發(fā)射電磁波 :雷達探測器會發(fā)射一定頻率的電磁波,這些波以光速傳播。 目標反射
探測器選擇指導
? 以下是選擇探測器的簡單說明: 1.確定應(yīng)用的要求。需要考慮的一些參數(shù)是: 光功率水平 入射光波長范圍 探測器放大器的電帶寬 應(yīng)用的機械要求,如:儀器的尺寸(是否需要小型探測器?);儀器的功耗
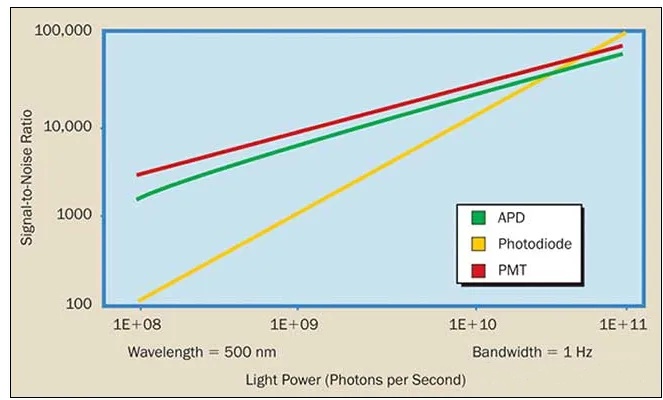
光電探測器選型噪聲問題
在設(shè)計探測器系統(tǒng)時,保持電帶寬盡可能接近所需帶寬至關(guān)重要。也就是說,如果光信號以10kHz的頻率變化,那么具有1MHz帶寬的探測器系統(tǒng)只會不必要地引入噪聲。 在任何光檢測應(yīng)用中,信號檢測的下限由
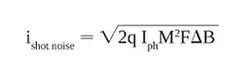
熱解粒子探測器與什么相似
熱解粒子探測器與某些類型的火災(zāi)探測器在功能和原理上有相似之處,但并非完全等同。以下是一些與熱解粒子探測器相似的探測器類型及其相似點: 煙霧探測器
被動紅外探測器與主動紅外探測器的原理比較
被動紅外探測器(Passive Infrared Detector, PIR)和主動紅外探測器(Active Infrared Detector, AID)是兩種常見的安全監(jiān)控設(shè)備,它們在防盜報警
被動紅外探測器和主動紅外探測器的區(qū)別
被動紅外探測器和主動紅外探測器是兩種常見的安全監(jiān)控設(shè)備,它們在防盜、監(jiān)控、邊界防護等方面有著廣泛的應(yīng)用。這兩種探測器的主要區(qū)別在于它們檢測紅外輻射的方式不同。 被動紅外探測器(PIR)
VirtualLab:通用探測器
摘要
通用探測器是VirtualLab Fusion中來評估和輸出電磁場任何信息的最通用工具。它能夠提供不同域(空間域和空間頻域)和坐標系(場與探測器位置坐標系)的信息。此外,通過使用非常靈活的內(nèi)置
發(fā)表于 08-06 15:20





 金屬探測器,Metal detectors
金屬探測器,Metal detectors











評論